Tokenization is the process of converting ownership rights of an asset into a digital token on a blockchain. This innovative method allows for the representation of both physical and digital assets in a secure, immutable, and easily transferable digital form.
Tokenization is transforming our approach to asset ownership and investment. By converting real-world assets or information into digital tokens, tokenization creates new investment opportunities, increases liquidity, and enhances transparency. In this article, we’ll explore the world of tokenization, examining its benefits, types of tokens, and the steps involved in tokenizing assets on a blockchain.
Benefits of Tokenization
Tokenization offers several benefits, including:
Increased Liquidity: Tokenization makes assets more easily tradable, increasing market liquidity. This is particularly important for illiquid assets, such as real estate or art, which can be difficult to buy and sell quickly.
Faster Transactions: Blockchain-based tokenized assets can be transacted 24/7, reducing processing times and enabling faster settlement.
Transparency: Tokenization enhances the transparency and traceability of asset ownership and transactions, reducing the risk of fraud and increasing trust in the system.
Fractional Ownership: Tokenization allows for fractional ownership of assets, opening up investment opportunities to a wider range of investors and enabling greater diversification.
Accessibility: Tokenization can make assets more accessible to a wider range of investors, including those in emerging markets or with limited financial resources.
Cost Savings: Tokenization can reduce the costs associated with traditional asset ownership, such as storage, maintenance, and transfer fees.
Global Reach: Tokenization enables assets to be traded globally, breaking down geographical barriers and expanding the pool of potential investors.
Programmability: Tokenized assets can be programmed with smart contracts to automate various processes, such as dividend distributions, voting rights, and compliance checks.
Enhanced Security: Blockchain technology provides robust security features, such as cryptographic encryption and decentralized consensus, reducing the risk of tampering and unauthorized access.
Types of Tokens in Blockchain Tokenization
There are four primary types of tokens in blockchain tokenization:
Security Tokens
- Represent ownership of traditional financial assets like stocks, bonds, or real estate.
- Subject to regulations and typically backed by tangible assets.
- Enable fractional ownership of assets, increasing accessibility for investors.
- Can be used to represent ownership in companies, funds, or other investment vehicles.
Utility Tokens
- Designed to provide access to specific functions within a decentralized platform.
- Do not represent ownership or equity in the underlying project or company.
- Can be used to incentivize user engagement within the platform, such as through rewards or discounts.
- Often used in decentralized applications (dApps) and decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms.
Crypto Tokens
- Digital assets are used for securely storing and transferring value.
- Often operate using smart contracts, enabling various functionalities within blockchain applications.
- Play a significant role in decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, such as lending, borrowing, and yield farming.
- Can be used as a store of value, a medium of exchange, or a unit of account.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
- Represent unique digital items such as art, collectibles, and virtual real estate.
- Use smart contracts to verify the authenticity and ownership of the digital assets.
- Have gained popularity with high-profile sales in the art and digital collectibles market.
- Can be used to represent ownership of unique physical assets, such as rare art or collectibles.
Steps to Tokenize Assets on Blockchain
To tokenize assets on a blockchain, follow these steps:
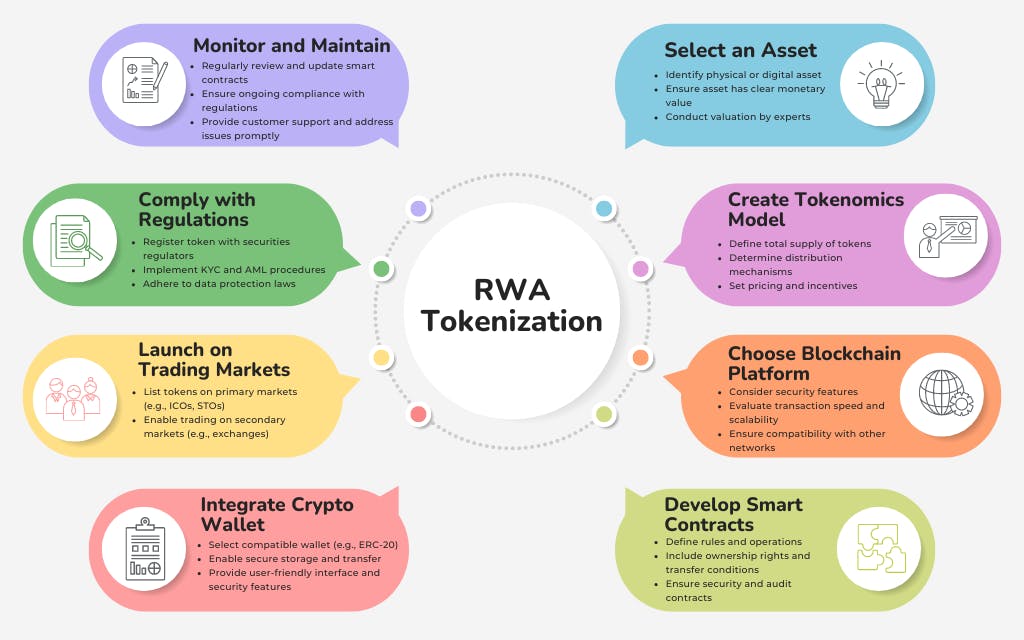
- Select an Asset: Identify the asset you want to tokenize. This can be a physical asset like real estate, art, or commodities, or a digital asset such as intellectual property or digital content. The chosen asset should have a clear monetary value and be suitable for fractional ownership. The valuation of the asset should be conducted by experts or appraisers who specialize in that particular type of asset.
- Create Tokenomics Model: Develop a comprehensive economic model for the token. This involves defining the total supply of tokens, how they will be distributed (e.g., initial distribution, ongoing issuance), pricing mechanisms, and any incentives for holding or using the tokens. The tokenomics model should align with the asset’s value and use case.
- Choose Blockchain Platform: Select a blockchain platform that supports asset tokenization. Consider factors such as security features, transaction speed, scalability, and compatibility with other blockchain networks and financial systems. Popular platforms include Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, and Polkadot.
- Develop Smart Contracts: Write smart contracts that define the rules and operations for the tokenized asset. Smart contracts should cover aspects like ownership rights, transfer conditions, dividend distributions, and any other relevant functionalities. Ensure that the smart contracts are secure and have been audited to prevent vulnerabilities.
- Integrate Crypto Wallet: Choose a cryptocurrency wallet that supports the token standard you are using (e.g., ERC-20 for Ethereum). Integrate this wallet to enable users to store, transfer, and manage their tokens securely. The wallet should be user-friendly and provide necessary security features like private key management and multi-factor authentication.
- Launch on Trading Markets: Once the tokens are created and the smart contracts are deployed, list the tokens on primary and secondary markets. Primary markets involve initial offerings, such as Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) or Security Token Offerings (STOs). Secondary markets include cryptocurrency exchanges where tokens can be traded between investors.
- Comply with Regulations: Ensure that the tokenization process adheres to all relevant legal and regulatory requirements. This may include registering the token with securities regulators, implementing Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) procedures, and adhering to data protection laws. Compliance is crucial to avoid legal issues and gain the trust of investors.
Real-World Examples of Asset Tokenization
St. Regis Aspen Resort Tokenization
In 2018, Elevated Returns, a New York-based asset management firm, successfully tokenized $18 million worth of shares in the St. Regis Aspen Resort in Colorado. Utilizing the Ethereum blockchain, they allowed accredited investors to purchase fractional ownership of the luxury hotel through digital tokens. This groundbreaking move demonstrated how real estate assets could be made more liquid and accessible, paving the way for similar tokenization projects in the future.
Andy Warhol’s “14 Small Electric Chairs”
In 2019, the art investment platform Maecenas partnered with Dadiani Syndicate to tokenize a 31.5% ownership stake in Andy Warhol’s painting “14 Small Electric Chairs.” This allowed investors to buy and trade fractional shares of the artwork using blockchain technology, making high-value art more accessible to a broader range of investors.
RealT: Tokenizing Real Estate
RealT tokenizes real estate properties, allowing investors to purchase fractional ownership in rental properties through blockchain technology. This enables investors to earn rental income and benefit from property appreciation without the need for traditional real estate investment methods.
Challenges and Limitations
While tokenization offers many benefits, it also presents several challenges and limitations, including:
Regulatory Uncertainty: The regulatory environment for tokenization is still evolving and uncertain, creating risks for investors and issuers.
Security Risks: Tokenized assets are vulnerable to security risks, such as fraud.
Liquidity Risks: Tokenized assets may lack liquidity, making it difficult to buy and sell.
Interoperability: Tokenized assets may not be compatible with existing financial systems and infrastructure.
Future Prospects
The future of tokenization looks promising as technology and regulatory frameworks continue to evolve. Innovations such as layer-2 scaling solutions and cross-chain interoperability are expected to address some of the current limitations, making tokenization more efficient and secure. Additionally, as regulatory clarity improves, more traditional financial institutions are likely to embrace tokenization, further legitimizing and expanding the market. This could lead to an even broader range of assets being tokenized, creating new opportunities for investors and transforming the financial landscape.
FAQs
1. What is tokenization in blockchain?
Tokenization is the process of converting ownership rights of an asset into a digital token on a blockchain. This allows assets, both physical and digital, to be represented in a secure, immutable, and easily transferable digital form.
2. What are the benefits of asset tokenization?
Asset tokenization offers several benefits, including increased liquidity, faster transactions, enhanced transparency, fractional ownership opportunities, accessibility to a wider range of investors, cost savings, global reach, programmability via smart contracts, and enhanced security through blockchain technology.
3. What are the types of tokens used in blockchain tokenization?
There are primarily four types of tokens used in blockchain tokenization: Security Tokens, Utility Tokens, Crypto Tokens, and Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs). Each serves different purposes and has distinct characteristics tailored to various asset types and functionalities.
4. How can assets be tokenized on a blockchain?
To tokenize assets on a blockchain, the process typically involves selecting the asset, creating a tokenomics model, choosing a suitable blockchain platform, developing smart contracts, integrating a crypto wallet, launching on trading markets, and ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
5. What are the challenges and limitations of asset tokenization?
Challenges include regulatory uncertainty, security risks, liquidity concerns, and interoperability issues with existing financial systems. Addressing these challenges is crucial for wider adoption and acceptance of tokenized assets.






